

CONTENTS
2......... PURPOSE OF THE PLAN.. 1
3......... WASTE MANAGEMENT POLICY
AND STRATEGIES.. 2
4......... LEGISLATION AND
GUIDELINES.. 2
5......... LICENCE OR PERMIT
REQUIREMENTS.. 4
5.1
Registration as a Chemical Waste Producer 4
5.2
Dumping licence to Public Filling Area. 4
5.3
Dumping permit for Marine Disposal of Excavated Mud/Sediment 4
5.4
Registration as a Waste Producer under the Construction Waste
Disposal Charging Scheme 5
6......... PROJECT
ORGANISATION.. 5
7......... INDIVIDUAL DUTIES AND
RESPONSIBILITIES.. 5
7.6
Environmental Officer (EO) / Engineer (EE) 6
7.7
Environmental Supervisor 7
7.8
Environmental Team (ET) /
Environmental Team Leader (ETL) 7
7.9
Subcontractors and other Employees. 7
8......... WASTE CLASSIFICATION AND
CONTROL MEASURES.. 7
8.1
Construction and Demolition (C&D) Materials. 8
9......... WASTE MONITORING AND
AUDITING.. 12
9.3
Record Keeping and Reporting. 15
11....... MITIGATION MEASURES IN
EIA.. 17
12....... MITIGATION MEASURES IN
EM&A Manual 17
APPENDICES
Appendix A
Gammon’s Health, Safety and
Environmental Policy
Appendix B
Organisation Structure for Environnemental
Management
Appendix C
Contact List
Appendix
D
Proforma of Yearly Summary Waste Flow
Table
Appendix
Appendix
F
Disposal Scenarios and Transportation Modes
Appendix
G
Proposed
Temporary Storage and Sorting Area for C&D
Materials
Appendix
H
Memo from Marine Fill Committee of CEDD
Appendix I
Control Procedures on Off-Site Disposal of C&D
Materials
Appendix J
Sample of CHIT Form
Appendix K
Protocol of Guidelines to Dump Truck Drivers
Appendix L
Sample of Daily Record Summary
Appendix
M
Environmental Mitigation Implementation Schedule for Waste
Management
Environmental
protection and sustainable development are part and parcel of the daily
operations of the Gammon Construction Limited (referred to hereinafter as the
GCL). GCL will initiate appropriate
actions in order to minimize, and where possible eliminate, the environmental
impact arising from the construction of this project.
Gammon
Construction Limited (GCL) has been awarded of the Contract No. HY/2012/07 –
Tuen Mun Chek Lap Kok Link – Southern
Connection Viaduct Section for Highways Department (HyD) of the Government of the Hong Kong Special
Administrative Region (HKSARG). The
Works to be executed comprise the design and construction of a dual 2-lane
elevated carriageway between the HZMB HKBCF and North Lantau Highway (NLH) with associated slip roads, as well as
modifications and realignment of sections of the NLH and
The Waste
Management Plan (WMP) has been prepared to describe the arrangements for
minimising the generation of construction and demolition (C&D) materials and
disposing of the surplus C&D materials during the course of the Works.
This
contract-specific WMP shall be deposited to the Director of Environmental
Protection in accordance with the Condition 2.10 of the
Environmental Permit No. EP-354/2009/A..
The WMP shall address the potential and actual
impacts and necessary mitigation measures in light of the preferred construction
programme and consists of the following:-
·
A review
of the ordinances, regulations, codes of practices as well as contractual
obligations that are applicable to the wastes arising from the
Works;
·
An
organisation chart setting out the roles and responsibilities of the GCL’s
personnel responsible for waste management and appropriate mitigation
measures;
·
An
analysis of timing, quantities and types of C&D materials are anticipated to
be generated in the course of the execution of the Works;
·
A
classification of C&D materials into inert portion (Public Fill) and
non-inert portion (C&D Waste);
·
Proposals for avoiding/minimizing, handling, recycling, reuse,
return, storage and disposal of C&D materials, chemical waste and general
refuse;
·
An
appraisal of the potential establishment on site of a sorting facility,
including the identification of potential area on-site of facilitate the waste
sorting;
·
A
proposal for maintaining the site in a clean and tidy
condition;
·
A
monitoring and auditing proposal to ensure that the requirements of the WMP are
properly implemented.
The principles of waste
management adopted in this project shall be in line with Gammon
Table 3.1 Core
Elements of Waste Management
|
Elements |
Ref.
Section |
|
Legislation and
Guidelines License or Permit
Requirements Project
Organisation Individual Duties and
Responsibilities Classification of Waste
& Control Measures Waste Monitoring and
Auditing Training Mitigation Measures in
EIA Mitigation Measures in EM&A
Manual |
4.0 5.0 6.0 7.0 8.0 9.0 10.0 11.0 12.0 |
The various waste management options shall be categorised in terms of
preference from an environmental viewpoint. The options considered to be more
preferable have the least impacts and are more sustainable in the longer
term. Hence, the hierarchy of waste
management is as follows:
·
Avoidance and
minimisation, i.e. not generating waste through changing or improving practices
and design;
·
Reuse of
materials, thus avoiding disposal;
·
Recovery and
recycling, thus avoiding disposal; and
·
Treatment and
disposal, according to relevant laws, guidelines and good
practice.
This hierarchy shall be used to evaluate waste management options, thus allowing maximum
waste reduction. Waste reduction
measures shall be introduced at the detailed planning stage and carried through
the construction activities, whenever possible, by careful purchasing control,
reuse of formworks and good site management. By reducing or eliminating over-ordering
of construction materials, waste is avoided and costs are reduced both in terms
of purchasing of raw materials and in disposing of
wastes.
The following legislation covers, or has some bearing upon, the
storage, collection, treatment and disposal of wastes in
·
Foreshore and Sea-bed (Reclamations) Ordinance (Cap
127);
·
Waste
Disposal Ordinance (Cap 354);
·
Waste
Disposal (Chemical Waste) (General) Regulation (Cap
354);
·
Land
(Miscellaneous Provisions) Ordinance (Cap
28);
·
Public
Health and Municipal Services Ordinance (Cap 132) – Public Cleansing and
Prevention of Nuisances (Urban Council) and (Regional Council) By-laws;
and
·
Dumping
At Sea Ordinance (Cap 466).
Other guiding documents which detail how the GCL should comply with
the regulations are as follows:-
·
Waste Reduction Framework Plan, 1998 to
2007,
Planning, Environment and Lands Bureau, Government Secretariat (5 November
1998);
·
2001 Review of the Waste Reduction Framework
Plan, Waste Reduction Committee;
·
Site Practice for Waste Reduction in
Construction Industry
(2001), Environmental Protection
Department;
·
Environmental Guidelines for Planning in Hong
Kong
(1990), Hong Kong Planning and Standards Guidelines,
·
New Disposal Arrangements for Construction
Waste
(1992), Environmental Protection Department & Civil Engineering
Department;
·
A Guide to the Registration of Chemical Waste
Producers (2001), Environmental Protection
Department;
·
Code of Practice on the Packaging, Labelling
and Storage of Chemical Wastes
(1992), Environmental Protection Department;
·
A Guide to the Control on Import and Export
of Waste
(1999), Environmental Protection Department;
·
Works
Bureau Technical Circular No. 10/92, Provision of Refuse Containment Booms in
Reclamation Contracts Involving Public Dumping, Works
Bureau;
·
Works
Bureau Technical Circular No. 2/93, Public Dumps, Works
Bureau;
·
Works
Bureau Technical Circular No. 2/93B, Public Filling Facilities, Works
Bureau;
·
Works
Bureau Technical Circular No. 16/96, Wet Soil in Public Dumps, Works
Bureau;
·
Works
Bureau Technical Circular No. 4/98 and 4/98A, Use of Public Fill in Reclamation
and Earth Filling Projects, Works Bureau;
·
Works
Bureau Technical Circular No. 25/99, 25/99A and 25/99C, Incorporation of
Information on Construction and Demolition Material Management in Public Works
Sub-committee Papers, Works Bureau;
·
Works
Bureau Technical Circular No 12/00, Fill Management; Works Bureau;
·
Works
Bureau Technical Circular No 19/01, Metallic Site Hoardings and Signboards,
Works Bureau;
·
Works
Bureau Technical Circular No 6/02 and 6/02A, Enhancement Specification for Site
Cleanliness and Tidiness, Works Bureau;
·
Works
Bureau Technical Circular No 12/2002, Specification Facilitating the Use of
Recycled Aggregates, Works Bureau;
·
Works
Bureau Technical Circular No 24/2004, Specification Facilitating the Use of the
Concrete Paving Units Made of Recycled Aggregates, Works
Bureau;
·
Environment, Transport and Works Bureau Technical Circular (Works) No
33/2002, Management of Construction and Demolition Material including Rock,
Environment, Transport and Works Bureau;
·
Environment, Transport and Works Bureau Technical Circular (Works) No
34/2002, Management of Dredged/Excavated Sediment, Environment, Transport and
Works Bureau;
·
Environment, Transport and Works Bureau Technical Circular (Works) No
15/2003, Waste Management on Construction Sites, Environment, Transport and
Works Bureau;
·
Environment, Transport and Works Bureau Technical Circular (Works) No
19/2005, Environmental Management on Construction Sites, Environment, Transport
and Works Bureau; and
·
Development Bureau Technical Circular (Works) No 6/2010, Trip-ticket
System for Disposal of Construction and Demolition Material, Development
Bureau.
Under the Waste Disposal (Chemical Waste) (General) Regulation, producers of chemical wastes must have
registration with Environmental Protection Department. The registration shall be applied for as
required.
The Land (Miscellaneous Provisions) Ordinance requires that dumping
licences are obtained by individuals or companies who deliver inert portion of
construction and demolition material (i.e. Public Fill) to Public Filling Areas.
The licences are issued by Civil Engineering Department under delegated powers
from the Director of Lands. The license shall be applied for as
required.
The Dumping at Sea Ordinance requires that dumping permits are
obtained by individuals or companies who deliver dredged/excavated marine
sediment to designated disposal sites. The permits are issued by Environmental
Protection Department under delegated powers from the Director of Environmental
Protection.
A billing account shall be opened with EPD prior to using Government
waste disposal facilities. Waste
shall be handled, transported, disposed and paid for in accordance with the
Charging Scheme.
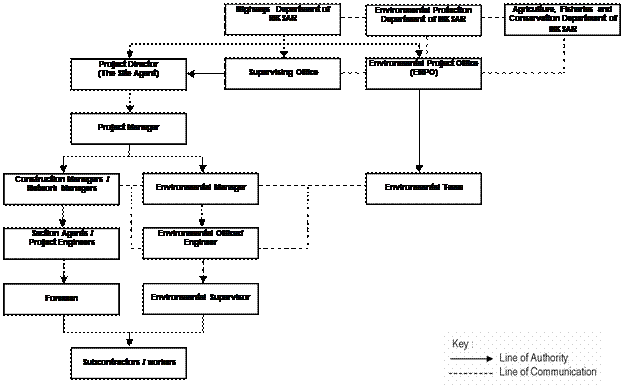
The organisational
structure for environmental management are in-line with the project management
during the course of the Works is presented in Appendix B, which identifies the major parties
with environmental responsibilities and illustrates their lines of
communication. Descriptions on the roles and responsibilities of these parties
are provided in the following sub-sections. The contact list for the
representatives of the concerned parties is given in Appendix C.
He is responsible to GCL’s
Executive Directors for overall planning, contract review, appointment of Site
Health Safety & Environmental (HS&E) Representative and other site
members for environmental matters.
He will ensure provision of adequate resources to address environmental
matters for the Project.
The Project Director has the following
responsibilities in relation to waste management:
-
·
Approving the
WMP;
·
Maintaining the overall control
of the Contract and oversee the implementation of the
WMP;
·
Ensuring that adequate resources
are provided for the efficient implementation of
WMP;
·
Reporting to Senior Management
of Company on all environmental matters whenever necessary;
and
·
Ensuring compliance of all
relevant waste management legislation throughout the duration of the
Contract..
The
Project Manager has the following responsibilities in relation to waste
management: -
·
the day-to-day overview of site
practices in relation to waste management;
·
directing Section Agents,
General Foremen and Foremen as appropriate in supervising and enforcing the
on-site mitigation measures;
·
reporting to the PM;
and
·
ensuring all waste records be
promptly available to the Environmental Manager for record and/or action as
necessary
Site Engineers/Site Agents/Foremen are
responsible for the following duties in relation to environmental
control:
·
coordinating waste management on
site, gather data about waste and keep up-dated record of waste movement on and
off site;
·
obtaining a list of potential
buyers or collectors of waste to be reused or recycled;
and
·
investigating potential re-use and
recycle opportunities of waste.
Site Agents/Foremen are responsible for the
following duties in relation to environmental
control:
·
assisting Environmental Manager
in all aspects of required waste management on
site;
·
supervising and monitoring the
works of workers including subcontractors in relation to waste management;
and
·
ensuring all waste containers and
storage areas are properly labelled.
The
Environmental Manager shall oversee the implementation and the performance of
the WMP and shall also be responsible
for:
·
the day-to-day overview of site
practices in relation to waste management on
site;
·
applying all necessary licences
in relation to waste
management;
·
reporting to the
PM;
·
coordinate with the Construction
Manager to ensure proper implementation of mitigation measures on waste
management;
·
conducting meetings/ briefings/
inductions/ tool-box talks with all sub-contractors, direct contractors,
specialist contractors, utility undertakers and employees to enhance
understanding of aims and contents of WMP;
and
·
preparing and submitting the Monthly
Summary Waste Flow Table (WFT), Yearly Summary WFT and Summary Table for Work
Processes or Activities Requiring Timber for Temporary
Works.
The
Environmental Officer/ Engineer shall assist the Environmental Manager to
oversee the implementation and the performance of the WMP and shall also be
responsible for:
·
assisting EnvM to disseminate information and requirement to the site
operative in connection with the implementation of the waste management
on-site;
·
monitoring the WMP
implementation, carrying out site
surveillance;
·
keeping environmental related
documents as well as assisting on training staff at different
levels;
·
assisting in the review and
update of the WMP, the Waste Flow Tables (WFT) and the summary table for the use
of timber during temporary works construction;
and
·
working closely with Site Engineers to
ensure the Contract is carried out in compliance with all waste related
contractual and legal requirements..
Site-resident
Environmental Supervisor (ES) will be appointed by the GCL. The duties of the
ES’s will include but not limited to the
following:
(a)
Assist the EO/ EE in carrying
out his duties;
(b)
Carry out daily site
environmental inspections based on a checklist approved by the SOR, and to
ensure that follow-up actions have been taken promptly against defects and
deficiencies identified;
(c)
Advise the EO/ EE on the upkeeping of environmental performance and standards of the
Site;
(d)
Attend the weekly environmental
walk;
(e)
Supervise and promote the
execution of environmental work on the Site;
(f)
Attend SSEMC meetings and SSEC
meetings; and
(g)
Conduct toolbox talks as
assigned by the GCL’s Agent after acquiring the
necessary.
The ET /ETL shall be an
independent environmental consultant from GCL. The ET
shall:
·
maintaining overall control of
the monitoring and professional
services;
·
reporting directly to the
Environmental Manager;
·
providing assistance and
guidance to the Contractor in the implementation of
WMP;
·
identifying the potential
hazardous waste whenever possible and take proactive actions before problems
arise;
·
providing briefing to the
project team as necessary on the waste management requirements;
and
·
carrying out Waste Management
Audit.
Every employee and subcontractor has the duty to carry out agreed
waste management practices as instructed by the Site Agent / Site Engineer.
Their duties are:
·
observing and implementing the
measures set out by this WMP;
·
following all environmental
related instructions given by the management staff of
GCL;
·
reporting any non-compliance of
the waste management measures; and
·
conducting the rectifying actions as
required in a timely and efficient manner.
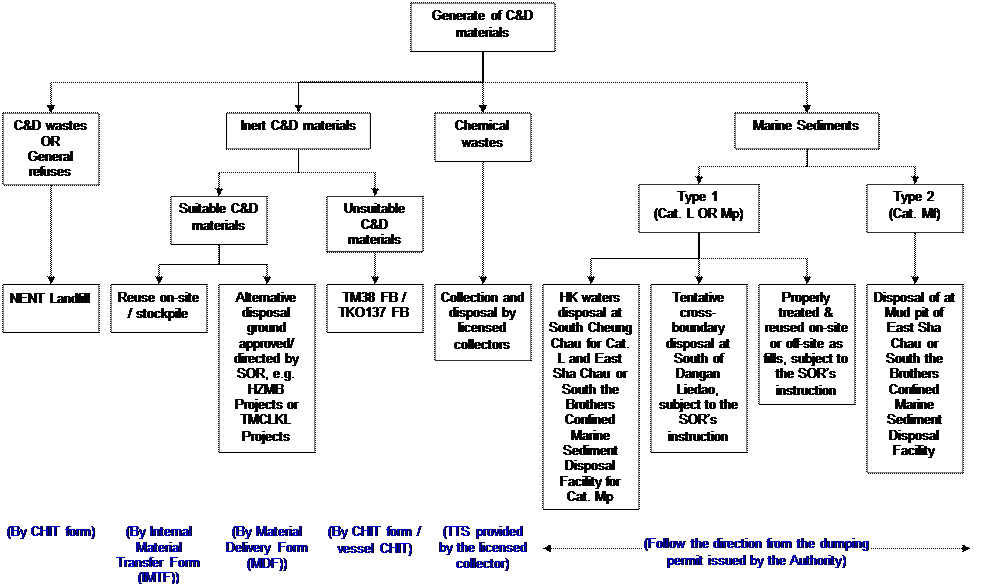
The waste generated from the construction activities shall be divided
into distinct categories based on their composition, as follows:
(a) Construction and demolition (C&D)
materials
(i)
Inert C&D materials
(ii)
Non-inert C&D materials
(b) Chemical wastes
(c) General refuses
(d) Dredged marine sediments
(i) Uncontaminated marine sediments (Cat. L
)
(ii)
Contaminated marine sediments (Cat. Mp
& Mf)
A
quantities of
excavated materials to be generated, reuse on- or offsite during works has been
estimated and shown in Appendix D.
The estimated quantities, types of the C&D materials and corresponding
disposal grounds will be updated monthly and indicated in the monthly programme for disposal of C&D materials, which will be
reported to the SOR via submissions of monthly waste flow tables as shown in Appendix
E. All
anticipated disposal scenarios and transportation modes are summarized in Appendix
F.
C&D materials comprise unwanted
materials generated during construction, including rejected structures and
materials, materials which have been over ordered or are surplus to
requirements, and materials used and discarded.
C&D material could be divided into two
categories according to whether they are inert or non-inert. Inert C&D
material are known as rock, rubble, boulder, earth, soil, sand, concrete,
asphalt, brick, tile, masonry and used bentonite,
where to be maximized the reuse of these materials within the Contract and to be
disposed of the surplus of these materials to other Contracts, subjected to the
approval or direction of Supervising Office Representative (SOR). Under any
circumstances that no site is able to receive the unsuitable C&D materials
for the filling purpose, GCL will apply to CEDD for the public fill reception
facilities (PFRF) as a back-up option.
Non-inert C&D material
are such as metal, timber, vegetation, packaging waste, organic material and all
recyclables and non-recyclables is called “C&D Waste”. C&D waste,
excluding recyclables, shall be disposed of at NENT
Landfill.
Recyclables are mainly metals, paper/cardboard packaging and
plastics. Plastics refer to plastic bottles/containers, plastic sheets/foam from
packaging material. Recyclables would be collected by
relevant recyclers. Non-recyclable materials are treated as general
refuse.
The following general low waste construction
designs and principles together with careful planning shall be adopted to
avoid/minimise C&D material generation. Such measures include:
-
(a)
Management of construction materials such that over-ordering, poor
storage and maintenance, mishandling as well as improper operation procedures
shall be avoided.
(b)
Restriction on use of hardwood such that softwood, metal props and/or
proprietary steel system shall be considered for false work and the shoring of
trenches and pits;
(c)
The
formwork shall be designed to maximise the use of standard wooden panels so that
high reuse levels can be achieved.
More durable alternatives such as steel formwork or plastic facing shall
be considered for repetitive areas to increase the potential for reuse.
(d)
C&D materials shall be, as much as possible and practicable,
separated into reusable items and materials to be disposed of or recycled. It
shall be conducted at the immediate working area to avoid loss/leakage and cross
contamination during handling.
(e)
All
C&D materials arising from or in connection with the construction and
demolition work shall be sorted on-site and be separated into different
categories for disposal at landfills, public filling areas, or reuse and
recycling as appropriate. The
sorting area may be revised from time to time in order to suit the construction
activities.
(f)
Useful materials such as timber, rubble and steel/metal shall be
segregated for reuse. For example formwork and timber shall be cleaned for
reuse, off-cuts of reinforcement shall be sorted into usable lengths and short
off cuts stacked for scrap metal.
Where it is no longer reusable, scrap steel and metal items will be
collected by recycling companies.
(g)
Segregated materials shall be temporarily stored at designated areas
for reuse on site. Steel will be stored at the reinforcement yards, timber at
the formwork yard and rubble in a stockpile (either covered or sprayed to
control dust). Cardboard and paper
packaging recovered from site shall be properly stockpiled in dry condition and
covered.
(h)
In order to avoid over-order of concrete, accurate calculation shall
be made prior to concrete pouring.
Close supervision shall also be arranged during concrete pouring to avoid
over-cast.
(i)
Surplus concrete shall be used for paving of temporary road or cast
of concrete blocks for bunding etc. as far as
practicable. In case immediate use
of surplus concrete cannot be identified, the surplus concrete will be
temporarily poured into designated surplus concrete pouring areas on site for
further disposal to public filling areas.
(j)
Entirely cover every stock of more than 20 bags of cement by
impervious sheeting and carry out the de-bagging, batching and mixing processes
in an area sheltered on the top and the 3 sides.
Damp and gather the waste cement bags for proper
disposal.
(k)
Used
bentonite shall only be disposed of at Public Fill
area.
GCL designate suitable
areas onsite for the storage, sorting and segregation of construction
waste. The areas that are
designated by GCL will be clearly defined with appropriate signage and barriers
(or similar) and allow for easy access by workers and vehicles. As the project progresses it is
anticipated that the designated areas will be reviewed depending upon
construction program requirements.
The areas designated by GCL will be sufficient for the amounts of
construction waste that are anticipated to be generated during the course of the
contract. The sorting mechanism is shown in Table 8.1. The tentative locations for the
temporary storage and sorting of C&D waste are shown in Appendix G.
Table 8.1
Sorting of C&D Materials
|
Type of C&D
Material |
Required Action |
|
Rock |
Reuse on site where possible or recycle off
site |
|
Excavated material |
Reuse on site where possible or dispose of at approved landfill
facility |
|
Excavated Marine
Deposits |
Dispose of offsite at approved
location |
|
Concrete |
Sorted and segregated onsite, reuse on site where possible or
recycle offsite |
|
Metal |
Segregate and recycle
offsite |
|
Paper/Cardboard
Materials |
Segregate and recycle
offsite |
|
Plastics |
Use recycling containers and recycle
offsite |
|
Aluminium Cans |
Use recycling containers and recycle
offsite |
|
Timber |
Reuse on site if possible, other segregate and recycle off
site |
|
Chemical Waste |
Store in approved containers and transport offsite for disposal
at an approved facility |
Chemical wastes are the substances defined by the Schedule 1 of the Waste Disposal (Chemical Waste) (General)
Regulation. Chemical wastes generated from the
construction sites will primarily arise from the maintenance of plant and
equipment. These may typically include oils, lubricants, paints and solvents.
Containers used for the storage of chemical waste
shall:
·
be
suitable for the substance they are holding, resistant to corrosion, maintained
in a good condition, and securely closed;
·
have a
capacity of less than 450 litres unless the specification have been approved by
the EPD; and
·
display a
label in English and Chinese in accordance with instruction prescribed in Schedule 2 of the Waste Disposal
(Chemical Waste)(General) Regulation.
The storage area for chemical wastes
shall:
·
be
clearly labelled and used solely for the storage of chemical
waste;
·
be
enclosed on at least three sides;
·
have an
impermeable floor and bunding, of capacity to
accommodate 110% of the volume of the largest container or 20% by volume of the
chemical waste stored in that area;
·
have
adequate ventilation;
·
be
covered to prevent rainfall entering (water collected within the bund must be
tested and disposed as chemical waste if necessary);
and
·
be
arranged so that incompatible materials are adequately
separated.
Disposal of chemical waste shall:
·
be via a
licensed waste collector;
·
be to an
off site facility licensed to receive chemical waste,
such as a recycling facility located in Yuen Long Industrial Estate or the
Chemical Waste Treatment Facility located in Tsing
Yi.
A
Spill Response Plan shall be prepared separately and implemented to deal with
any accidental spillage of chemicals on site. The spill response plan should contain
procedures for:
·
Spill
prevention and precaution
·
Response
actions
·
Spill
clean up and
disposal
General
refuses include food wastes, non-recyclable materials (including waste
paper/cardboard packaging, plastics and timber) and other debris arising from
various construction activities, site workforce and site
housekeeping.
General refuses shall be disposed of at NENT Landfill.
Measures that encourage waste
avoidance/minimization
include:
·
Reducing the number of photo copies to a minimum and by copying on
both sides of paper for internal documents and external documents where
appropriate;
·
Preventing over-ordering of office equipment and
consumables;
·
Procuring green office equipment and consumables in terms of energy
efficiency, recycled content and durability, etc;
·
Providing drinking facility and encouraging employees to bring their
own cup; and
·
Discouraging take-out food.
Additional measures that facilitate
reuse/recycling
and orderly disposal include:
·
Deploying sufficient recycle bins at convenient locations to
facilitate collection of recyclables including wasted aluminium cans, plastic
bottles and cardboard and papers packaging;
·
Deploying sufficient refuse collection bin at convenient locations to
facilitate collection of non-recyclables for disposal at landfills;
and
·
Participating local collection scheme (e.g. scheme launched by
District Board) if available.
Marine
sediment means excavated from the Works of the foundation and associated
substructures at the sea. It could be classified as
contaminated and uncontaminated based on its contamination level with reference
to Chemical Exceedance Level (CEL) laid down in the
Appendix A of the ETWB TCW No. 34/2002. The excavation and disposal of marine sediments
generated shall be minimized from the Works in this
Contract,
e.g. only from the excavation of the foundation and the associated substructures
such as the piles, pile caps and piers. In events that dredging/ excavation of
marine sediment are unavoidable, the GCL shall handle/ process such marine
sediment in accordance with the procedures given in ETWB TCW No. 34/2002. GCL
will apply to the EPD for all valid permits and licenses in accordance with only
dispose of the marine sediment at the designated disposal facilities as directed
by the Director of Environmental Protection and/or the Marine Fill Committee
(MFC) unless otherwise agreed or ordered in writing by the Supervising Officer.
The copy of memo from Marine Fill Committee of CEDD granting the allocations for
the sediment disposal space is attached in Appendix
H.
In case of disposal of any amount of the marine sediment in Hong Kong
waters, the dumping of sediments shall be strictly within the designated
sediment disposal sites and shall be controlled through a dumping permit issued
under the Dumping at Sea Ordinance (Cap 466), or called a DASO permit, by the
Director of Environmental Protection. Dumping shall take place at sub-areas
within the sediment disposal sites, the locations of which will be changed from
time to time as notified by the Director of Environmental Protection through the
Supervising Officer.
Subject to the instruction of SO, notwithstanding whether the GCL
elects to dispose of any or all dredged/excavated marine sediments at the
designated sediment disposal sites in Hong Kong, the GCL will apply for approval
to relevant authorities in Mainland and Hong Kong for the cross-boundary
disposal of Cat. L and Mp
sediments at the tentative disposal site of South Dangan Liedao (擔杆列島). This cross-boundary disposal option shall only
proceed with the Supervising Officer’s instruction. In the event that the
approval of cross-boundary disposal is not obtained in a timely manner, Cat. L and Mp sediments
would be arranged to dispose of at South Cheung Chau Open Sea Sediment Disposal
Area and East Sha Chau or South of the Brothers Marine Sediment Disposal
Facility as a fallback option to be authorized by
Supervising Officer, EPD and CEDD-MFC.
In
cases that off-site disposal of marine sediment in Hong Kong Water required, GCL
shall apply for the allocation of a sediment disposal site in the name of
Highways Department of the HKSAR, and marine loading permits under Dumping at
Sea Ordinance (Cap. 466) (DASO) for the disposal of marine sediment at the
designated disposal facilities in Hong Kong.
The marine sediment of Category M failing
biological tests as defined in ETWB TC(W) No. 34/2002 shall be disposed of
in
CEDD-MFC's designated contaminated mud pits in Hong Kong waters, at mud pit of
East Sha Chau or South of the Brothers Marine Sediment Disposal Facility as
allocated
by CEDD-MFC. GCL shall place the contaminated mud at a location and in a manner
as directed on site by the CEDD management team. GCL shall proceed with the
disposal operation as instructed by the management team and in accordance with
the relevant sections of the Requirements of the Contaminated Mud Pit Management
Scheme which may be modified from time to time by the management team. GCL shall
not carry out any dumping without permission of the management team or when the
management team is not in operation. GCL will carry out the dumping operation in
strict accordance with the method statement agreed by the Licensing
Authority.
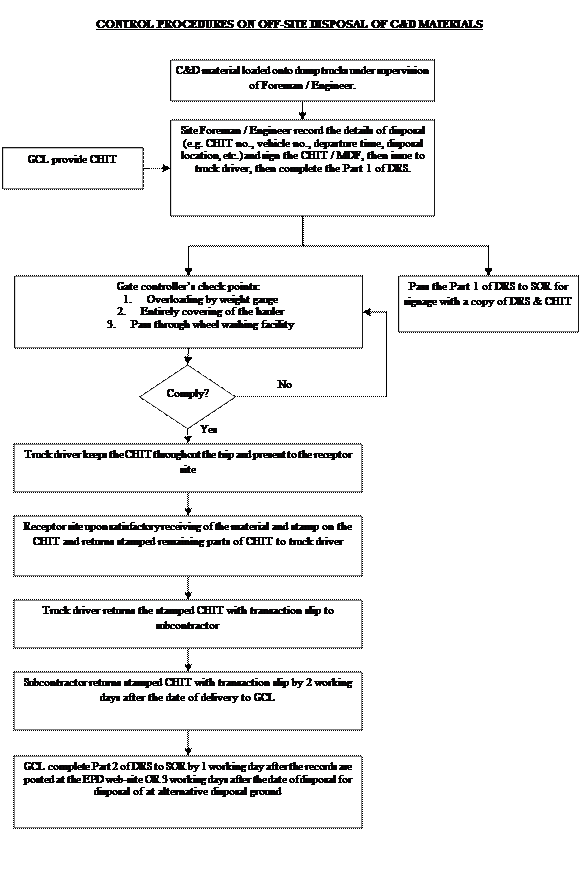
In accordance with DEVB TC(W) No. 6/2010,
with tender invitation was on or after 1 November 2010, the administration of
CHIT/ DDF was streamlined. CHIT in lieu of the bar-coded Disposal Delivery Form (DDF) should be used at
all prescribed facilities, i.e. public fill reception facilities,
sorting facilities, outlying island transfer facilities and landfills. Moreover,
under the Construction Waste Disposal Charging Scheme, GCL registered with EPD a
disposal account and will adopt the CHIT as the enhanced control of C&D
material disposal. The control procedure on off-site disposal of C&D
materials is shown in Appendix I. The sample of CHIT is given in Appendix
J.
Every C&D material disposal trip to the public fill reception
facilities and designated landfill shall be controlled under the trip-ticket
system as per the DEVB TC(W) No. 6/2010 in order to
avoid fly-tipping. Appendix G gives the site procedure for the TTS operation.
For disposal of chemical wastes, the trip-ticket system as per the
Waste Disposal (Chemical Waste) Regulation in which licensed collector will be
employed and the chemical wastes be disposed of at
designated chemical waste treatment facility.
GCL will inform all truck drivers engaged for removal
of C&D materials from the Site of the
following particular points:
·
Each truck carrying C&D
materials leaving the Site for a disposal ground must bear a duly completed
CHIT, irrespective of the location and nature of the disposal ground;
and
·
The C&D materials must be
disposed of at the disposal grounds stipulated in the Contract or directed by
the SOR or alternative disposal grounds approved by the
SOR.
GCL
would formulate a guiding protocol for truck
drivers being engaged and give all of them a copy for their information. Where
necessary, a tool box talk relating to the protocol will be given to all engaged
driver. The protocol is shown in Appendix
J.
GCL
shall arrange weekly inspection attended by the Environmental Officer and SOR to
inspect the site to ensure satisfactory performance on compliance with the WMP
with due regards to the followings:
(a)
Inert
C&D materials suitable for recycling into aggregates are recovered and
delivered to Tuen Mun Area
38 or other designated recycling facilities as notified by the
SOR or
the Public Fill Committee (Port Works Division of CED);
(b)
A
disposal recording system is operating satisfactorily for recording C&D
materials removed from the Site;
(c)
On-site sorting of C&D materials is properly carried out to
recover inert C&D materials and reusable and/or recyclable materials before
disposal;
(d)
Paper/cardboard packaging, and metals including aluminium cans are
recovered and collected; and
(e)
Plastic
bottles/containers or plastic sheets/foam from packaging are collected as far as
possible for recycling.
GCL may
arrange the
weekly inspection on waste management performance to be carried out along with
the weekly safety walks for safety or other site
inspections.
GCL shall prepare and agree with the SOR a comprehensive checklist for use during weekly inspections on waste
management. The defects or deficiencies identified during the weekly inspection
on waste management together with their respective locations and the
corresponding due dates for rectification as set by the
SOR nominated site representative should be entered in a summary table
of follow-up actions similar to the one established for weekly safety walks for
monitoring of the rectification progress. GCL may need to prepare more than one
comprehensive checklist to suit the variety of works at various portions of the
Site. It is recommended that items
covered in the checklist should primarily
address:-
(a)
the physical conditions of the Site (e.g. housekeeping, site tidiness
and cleanliness, etc.);
(b)
the adequacy of measures applied to each category of waste;
and
(c)
the availability/accessibility/maintenance of waste management
facilities.
Immediately after the weekly inspection, the
summary table of follow-up actions shall be agreed and signed by both the
assigned person and the SOR and a copy should be kept by the
SOR for monitoring of the progress of rectification and for payment. GCL
shall take prompt action to rectify the deficiencies identified and shall report
the status of action taken before the forthcoming weekly inspection.
Should deficiency
with regard to
waste management affairs persists,
the Event Contingency Plan as detailed below shall be triggered. Non-compliance shall include the
following situations:
·
Infringement of legal requirements with respect to waste issues.
·
Persistent outstanding of control measures stated in the WMP as
identified during the site inspection or
audit.
·
Overloading of dump truck
Table 9.1
Action Plan for Non-Compliance
|
Day |
Action |
GCL |
SOR | |
|
1. |
1 |
Create a new non-compliance record within 1 working day after
making an observation during a site audit accompanied by Environmental
Officer or his delegate.
Environmental Officer sends a Notice of Non-Compliance (NNC) to the
Project Manager / Site Agent.
The NNC would include the observations and the reasons for
non-compliance. |
|
|
|
2. |
2 |
Propose corrective actions within 1 working day after the
receipt of the NNC. |
|
|
|
3. |
2 |
Review and agree with the proposed corrective actions and make
additional recommendations as
required. |
|
|
|
4. |
2 |
Implement the proposed corrective actions once they have been
agreed. |
|
|
|
5. |
- |
Check the implementation of the corrective actions at the next
site audit. Close the
non-compliance record if the implementation of the corrective actions is
satisfactory. |
|
|
|
6. |
- |
Propose preventive actions within 3 working days after the
closure of the non-compliance
record. |
|
|
![]() Action
party
Action
party
![]() Comments on the
non-compliance record where applicable.
Comments on the
non-compliance record where applicable.
ET shall check whether GCL has followed the relevant contract
specifications and the procedures specified under the laws of
Table 9.2 Waste
Management Checklist
|
Activities |
Timing |
Monitoring
Frequency |
If
non-compliance, Action Required |
|
All
necessary waste disposal permits or licences
have been obtained |
Before
the commencement of demolition
works |
Once |
Apply
for the necessary permits/ licences prior to
disposal of the waste. The ET shall ensure that corrective action has been
taken. |
|
Only
licensed waste haulier are used for
waste collection. |
Throughout
the works |
Weekly |
The
ET shall inform the ER and IEC of the noncompliance. The ER shall instruct
the Contractor to use a licensed waste haulier.
The Contractor shall temporarily suspend waste collection of that
particular waste until a licensed waste haulier
is used. Corrective action shall be undertaken within 48
hours. |
|
Records
of quantities of wastes generated, recycled and disposed are properly
kept. For demolition material/waste, the number of loads for each day
shall be recorded (quantity of waste can then be estimated based on
average truck load. Should landfill charging be implemented, the receipts
of the charge could be used for estimating
the quantity). |
Throughout
the works |
Weekly |
The
Contractor shall estimate the missing data based on previous records and
the activities carried out. The ET shall audit the results and forward to
the ER and IEC for approval. |
|
Wastes
are removed from site in a timely manner. General refuse is collected on a
daily basis. |
Throughout
the works |
Weekly |
The
ET shall inform the ER and IEC of the noncompliance. The ER shall instruct
the Contractor to remove waste
accordingly. |
|
Waste
storage areas are properly cleaned and do not cause windblown litter and
dust nuisance. |
Throughout
the works |
Weekly |
The
ET shall inform the ER and IEC of the noncompliance. The ER shall instruct
the Contractor to clean the storage area and/or cover the
waste. |
|
Different
types of waste are segregated in different containers or skip to enhance
recycling of material and proper disposal of
waste. |
Throughout
the works |
Weekly |
The
ET shall inform the ER and IEC of the noncompliance. The ER shall instruct
the Contractor to provide separate skips/ containers. The Contractor shall
ensure the workers place the waste in the appropriate
containers. |
|
Chemical
wastes are stored, handled and disposed of in accordance with the Code of
Practice on the Packaging, Handling and Storage of Chemical Wastes,
published by the EPD. |
Throughout
the works |
Weekly |
The
ET shall inform the ER and IEC of the noncompliance. The ER shall instruct
the Contractor to rectify the problems immediately. Warning shall be given
to the Contractor if corrective actions are not taken within 24 hrs and the Waste Control Group of the EPD shall be
identified. |
|
Demolition
material/waste in dump trucks are properly
covered before leaving the
site. |
Throughout
the works |
Weekly |
The
ET shall inform the ER and IEC of the noncompliance. The ER shall instruct
the Contractor to comply. The Contractor shall prevent trucks shall
leaving the site until the waste are properly
covered. |
|
Wastes
are disposal of at licensed
sites. |
Throughout
the works |
Weekly |
The
ET shall inform the ER and IEC of the noncompliance. The ER shall warn the
Contractor and instruct the Contractor to ensure the wastes are disposed
of at the licensed sites. Should it involve chemical waste, the Waste
Control Group of EPD shall be
notified. |
GCL shall keep adequate and proper records such as delivery dockets and measurement records relating to
the implementation of the WMP. The
records shall include trip-ticket, completed inspection checklists and training
records.
Daily Record Summary (DRS) shall be filled by designated persons.to
record every truck for delivery of C&D materials. The sample of DRS is given
in Appendix
L.
As
part of the WMP,
a mechanism
shall be established to record the quantities of C&D materials generated
each month, using the monthly summary “Waste Flow Table” (WFT) as given in Appendix
E.
Estimated quantities of
C&D materials that will be generated each year from the site the GCL should
also be provided, using the yearly summary WFT as given in Appendix
D. The yearly summary WFT covering the whole construction period
shall be included in the WMP and updated on yearly basis, throughout the
construction period in order to account for the revised works programme and
latest outturn on the quantities of C&D materials generated from the
site.
To ensure the effectiveness
of the Trip-Ticket System, the following item will be discussed at every Site
Safety and Environmental Management Committee meeting, and Site Safety and
Environmental Committee meeting or ad-hoc meetings on as-needed
basis:
1. Review the site management plan
and implementation of the TTS, and identify areas for
improvement;
2. Audit the quantity of C&D
materials removed from the Site (based on the DRS and survey records) against
the quantities of C&D materials delivered to the disposal ground designated
in the Contract (e.g. based on EPD website) and directed or approved by the
Supervising Officer;
3. Review incidents of
non-compliance and discuss the necessary follow-up actions for TTS;
and
4. Monitor the follow-up action on
defects and deficiencies
identified.
The Environmental Officer and other site personnel (if they have not attended similar course
before) shall be arranged to attend training on waste management organised by
training institutes or organisations as considered
appropriate.
The Environmental Officer shall arrange and provide training on waste
management in the site-specific induction and its refresher training for all
persons employed by the GCL or his subcontractor on the Works or in connection with the Contract. The training should
cover the waste management policy, targets, measures for on-site sorting of
C&D materials and measurement on waste management performance on the Site.
According to ER requirement, induction training shall be carried out within
first 2 days of the employment and refreshment training shall be carried out by
every 6 months.
The Environmental Officer is allowed to develop and provide toolbox
talks for the topic on on-site sorting of C&D materials to promote the workers
The Section 12.6 of the EIA Report gives recommendations on
mitigation measures of waste management. The recommendations were extracted to
form an implementation schedule particularly for waste management during
construction phase and the schedule is shown in Appendix
M.
The Section 8.1.2 of the EM&A Manual gives recommendations on
mitigation measures of waste management, which
are:
·
The waste management hierarchy below should be strictly followed.
This hierarchy should be adopted to evaluate the waste management options in
order to maximise the extent of waste reduction and cost reduction. The records
of quantities of waste generated, recycled and disposed (locations) should be
properly documented.
·
A trip-ticket system should be established in accordance with
DEVB TC(W) No.
6/2010 and Waste Disposal (Charges for Disposal of Construction Waste)
Regulation to monitor the disposal of public fill and solid wastes at public
filling facilities and landfills, and to control fly-tipping. A trip-ticket
system would be included as one of the contractual requirements for the
Contractor to strictly implement. The Engineer would also regularly audit the
effectiveness of the system.
·
A recording system for the amount of waste generated, recycled and
disposed (locations) should be established. The future Contractor should also
provide proper training to workers regarding the appropriate concepts of site
cleanliness and waste management procedures, e.g. waste reduction, reuse and
recycling all the time.
·
The CEDD should be timely notified of the estimated spoil volumes to
be generated and the Public Fill Committee should be notified and agreement sort
on the disposal of surplus inert C&D materials e.g. good quality rock during
detailed design of the TM-CLKL project. Wherever practicable, C&D materials
should be segregated from other wastes to avoid contamination and to ensure
acceptability at public filling areas or reclamation
sites.
·
The extent of cutting operation should be optimised where possible.
Earth retaining structures and bored pile walls should be proposed to minimise
the extent of cutting.
·
Inert C&D materials from slopes and road pavement will be reused
for construction of the raised platform for the toll
plaza.
·
C&D materials generated by construction of cut slopes along NLH
at
·
The surplus surcharge should be transferred to a fill
bank.
·
Rock armour from the existing seawall should be reused on the new
sloping seawall as far as possible.
·
The site and surroundings shall be kept tidy and litter
free.
·
No waste shall be burnt on site.
·
Make provisions in contract documents to allow and promote the use of
recycled aggregates where appropriate.
·
Prohibit the Contractor to dispose of C&D materials at any
sensitive locations e.g. natural habitat, etc. The Contractor should propose the
final disposal sites in the EMP and WMP for approval before
implementation.
·
Stockpiled material shall be covered by tarpaulin and /or watered as
appropriate to prevent windblown dust and surface run
off.
·
Excavated material in trucks shall be covered by tarpaulins to reduce
the potential for spillage and dust
generation.
·
Wheel washing facilities shall be used by all trucks leaving the site
to prevent transfer of mud onto public
roads.
·
Dredged marine mud shall be disposed of in a gazetted marine disposal
ground under the requirements of the Dumping at Seas
Ordinance.
·
Standard formwork or pre-fabrication should be used as far as
practicable so as to minimise the C&D materials arising. The use of more
durable formwork or plastic facing for construction works should also be
considered. The use of wooden hoardings should be avoided and metal hoarding
should be used to facilitate recycling. Purchasing of construction materials
should be carefully planned in order to avoid over-ordering and
wastage.
·
The Contractor should recycle as many C&D materials (this is a
waste section) as possible on-site. The public fill and C&D waste should be
segregated and stored in separate containers or skips to facilitate the reuse or
recycling of materials and proper disposal. Where practicable, the concrete and
masonry should be crushed and used as fill materials. Steel reinforcement bar
should be collected for use by scrap steel mills. Different areas of the sites
should be considered for segregation and storage
activities.
·
All falsework will be steel instead of
wood, as far as possible.
·
Chemical waste producers should register with the EPD. Chemical waste
should be handled in accordance with the Code of Practice on the Packaging,
Handling and Storage of Chemical Wastes as
follows:
-
Suitable for the substance to be held, resistant to corrosion,
maintained in good conditions and securely
closed;
-
Having a capacity of <450L unless the specifications have been
approved by the EPD; and
-
Displaying a label in English and Chinese according to the
instructions prescribed in Schedule 2 of the
Regulations.
-
Clearly labelled and used solely for the storage of chemical
wastes;
-
Enclosed with at least 3 sides;
-
Impermeable floor and bund with capacity to accommodate 110% of the
volume of the largest container or 20% by volume of the chemical waste stored in
the area, whichever is greatest;
-
Adequate ventilation;
-
Sufficiently covered to prevent rainfall entering (water collected
within the bund must be tested and disposed of as chemical waste, if necessary);
and
-
Incompatible materials are adequately
separated.
·
Waste oils, chemicals or solvents shall not be disposed of to
drain;
·
Adequate numbers of portable toilets should be provided for on-site
workers. Portable toilets should be maintained in reasonable states, which will
not deter the workers from utilising them. Night soil should be regularly
collected by licensed collectors.
·
General refuse arising on-site should be stored in enclosed bins or
compaction units separately from C&D and chemical wastes. Sufficient
dustbins shall be provided for storage of waste as required under the Public
Cleansing and Prevention of Nuisances By-laws. In addition, general refuse shall
be cleared daily and shall be disposed of to the nearest licensed landfill or
refuse transfer station. Burning of refuse on construction sites is
prohibited.
·
All waste containers shall be in a secure area on hard standing;
Aluminium cans are usually collected and recovered from the waste stream by
individual collectors if they are segregated and easily accessible. Separately
labelled bins for their deposition should be provided as far as
practicable.
·
Office wastes can be reduced by recycling of paper if such volume is
sufficiently large to warrant collection. Participation in a local collection
scheme by the Contractor should be advocated. Waste separation facilities for
paper, aluminium cans, plastic bottles, etc. should be provided
on-site.
·
Training shall be provided to workers about the concepts of site
cleanliness and appropriate waste management procedure, including waste
reduction, reuse and recycling.
|
APPENDIX A Gammon’s Health, Safety and
Environmental Policy |




|
APPENDIX
B Organisation Structure for Environnemental
Management |
APPENDIX C Contact
List |
|
Contact List |
Telephone
No. |
|
Project Proponent – Highway Department HZMB
Office |
|
|
Employer’s Rep. – Mr. Johnny CHAN
|
2762 4976 |
|
Environmental Team - Environmental Resources Management |
|
|
Project Director – Mr. Craig A
REID |
2271 3179 |
|
ET Leader – Mr. Jovy
TAM |
2271
3113 |
|
Gammon Construction Ltd. |
|
|
Project Director – Mr. Andrew VENESS |
2750 0278 |
|
Deputy Project Director – Mr. Chris MA |
2750 0183 |
|
Engineering Director – Mr. John CLARK |
2750 0178 |
|
Senior Construction Manager – Mr. Nigel KING |
2750 0183 |
|
Construction Manager – Mr. Hans SUNDSTROM |
9300 7636 |
|
Construction Manager – Mr. W.T. HO |
6111 2176 |
|
Construction Manager – Mr. Wing LAW |
9655 0672 |
|
Project Manager – Mr. Patrick
CHAN |
9488 2979 |
|
Project Manager – Mr. K.M.
CHAING |
9360 0586 |
|
Safety
Manager – Mr. C.Y.
LAU |
9022 1273 |
|
Environmental Manager – Mr. Brian KAM |
9456 9541 |
|
Environmental
Officer – Mr. Roy
LEUNG |
6468 7650 |
|
Environmental Protection
Department |
|
|
EPO-RS(52) – Ms. Connie
WONG |
2516 1782 |
|
APPENDIX D Proforma of Yearly Summary
Waste Flow
Table |
Contract No. : HY/2012/07
Tuen Mun-Chek Lap Kok
Link – Southern Connection Viaduct
Section
Yearly Summary Waste Flow Table
Estimation
|
Year |
Estimated (Est.) Annual Quantities of Inert C&D
Materials |
Estimated (Est.) Annual Quantities of C&D
Wastes |
Estimated (Est.) Annual Quantities of
Recyclables | |||||||||||
|
(a)=(b)+(c)+ (d)+(e) Total Quantity
Generated |
(b) Hard Rock & Broken Concrete |
(c) Reused in the
Contract |
(d) Reused in other
Projects |
(e) Disposed as Public Fill (see Note
6) |
(f) Import Fill |
(g) Marine Sediment |
(h) Chemical Waste (in '000 kg) |
(i) Others, e.g. general refuse disposed at
Landfill (in |
(j) Metals (in |
(k) Paper/ cardboard
packaging |
(l) Plastics | |||
|
Cat. L |
Cat. Mp |
Cat. Mf | ||||||||||||
|
(in
'000m3) |
(in
'000m3) |
(in
'000m3) |
(in
'000m3) |
(in '000m3) |
(in '000m3) |
(in |
(in |
(in |
(in |
(in |
(in '000 kg) |
(in |
(in | |
|
Est. |
Est.. |
Est. |
Est.. |
Est. |
Est. |
Est. |
Est. |
Est. |
Est. |
Est. |
Est. |
Est. |
Est. | |
|
2013 |
53.108 |
26.554 |
26.554 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
1,000 |
-- |
2 |
-- |
|
2014 |
41.144 |
12.711 |
15.723 |
12.711 |
-- |
-- |
9.524 |
2.381 |
1.429 |
0.1 |
1,800 |
-- |
10 |
3 |
|
2015 |
58.021 |
1.63 |
56.114 |
0.277 |
-- |
-- |
10.476 |
2.619 |
1.571 |
0.1 |
1,800 |
-- |
10 |
3 |
|
2016 |
30.615 |
-- |
30.615 |
-- |
-- |
1.249 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
0.1 |
1,000 |
-- |
5 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Grand Total |
182.888 |
40.895 |
129.006 |
12.988 |
-- |
1.249 |
20.0 |
5.0 |
3.0 |
0.3 |
5,600 |
-- |
27 |
9 |
Notes:
(1)
The waste flow table shall also include C&D materials that are
specified in the Contract to be imported for use at the
Site.
(2)
Plastic refer to plastic bottles/containers, plastic sheets/foam from
packaging material
(3)
Broken concrete for recycling into
aggregates
(4)
The Yearly Waste Flow Table will be updated if there is any
changed.
(5)
Highlighted in yellow for any updated
(6)
GCL would
maximize reusing C&D material as far as possible. Public fill is a fall back
option for unsuitable material disposal, if
any.
|
APPENDIX E Proforma of Monthly Summary
Waste Flow
Table |
Contract No. : HY/2012/07
Tuen Mun-Chek Lap Kok
Link – Southern Connection Viaduct Section
Monthly Summary Waste Flow Table for ________ (Year)
|
Month\Material |
Actual
Quantities of Inert C&D Materials
Generation |
Actual
Quantities of C&D wastes
Generation |
Actual
Quantities of Recyclables
Generation | |||||||||||
|
Total
Quantity Generated |
Hard
Rock and Large Broken Concrete |
Reused
in the Contract |
Reused
in other Projects |
Disposed
as Public Fills |
Imported
Fill |
Marine
Sediment, Cat. L |
Marine
Sediment, Cat. Mp |
Marine
Sediment, Cat. Mf |
Chemical
Waste |
General
Refuse |
Metals
|
Paper/
cardboard packaging |
Plastics | |
|
Unit |
('000m3) |
('000m3) |
('000m3) |
('000m3) |
('000m3) |
('000m3) |
('000m3) |
('000m3) |
('000m3) |
('000Kg) |
('000Kg) |
('000Kg) |
('000Kg) |
('000Kg) |
|
Jan |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Feb |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mar |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Apr |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
May |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jun |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SUB-TOTAL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jul |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aug |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sep |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Oct |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nov |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TOTAL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Notes:
1
- The waste flow table shall also include C&D materials that are specified
in the Contract to be imported for use at the
Site.
2
- Plastics refer to plastic bottles/containers, plastic sheets/foam from
packaging material.
3
- Broken concrete for recycling into
aggregates.
|
APPENDIX F Disposal Scenario
and Transportation Models |
|
APPENDIX G Proposed Temporary Storage and Sorting Area for C&D
Materials |
|
APPENDIX H Memo from Marine Fill Committee of CEDD |
|
APPENDIX I Control Procedures on Off-Site Disposal of C&D
Materials |
|
APPENDIX J Sample of CHIT Form |

|
APPENDIX K Protocol of Guidelines to Dump Truck Drivers |
合約編號HY/2012/07
屯門至赤鱲角連接路 -南面連接路高架道路段
泥車離開地盤環保要點
運泥車於離開地盤前,司機需注意事項:
1.
運泥車上的建築廢物已經篩選分類;
2.
離開地盤範圍前必須確保機動蓋掩或使用帆布完全蓋好車斗。否則需卸下物料並離開地盤;
3.
離開地盤範圍前檢查磅錶,切勿超越負荷;
4.
離開地盤範圍前必先沖洗車轆;
5.
已填好運載記紀錄票上的所有資料;及
6.
必須將運載記錄票上的第一聯交給駐地盤監工人士,方可離開。
本人明白上述環保要點,並會遵守。
簽名:
司機姓名:
公司名稱:
車牌:
日期:
|
APPENDIX L Sample of Daily Record Summary |
A sample of “Daily Record
Summary” to record daily disposal of construction & demolition (C&D)
materials from the Site
(1) Contract no. &
title:
HY/2012/07 - Tuen Mun Chek Lap Kok Link – Southern Connection Viaduct
Section
(2) Date of disposal:
_______________________________________________
(3) Designated disposal
ground(s): (a)
(b)
others
(4) Approved alternative
disposal
grounds:
|
CHIT / DDF Serial no. |
Vehicle registration mark |
Approx. vol. (e.g. Full/ Three Quarter/ Half/ One
Quarter |
C&D material type (e.g. inert or non
inert) |
Disposal ground |
Signature & Name of the GCL’s Designated person before
departure |
Departure time from site |
Signature & Name of the SO’s staff before departure or
other time as agreed between Engineer’s Representative and the
GCL1 |
Actual disposal ground |
Arrival time at disposal ground |
Remark |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ß----------------------------------------------------------------------------Part
1 2
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------à |
ß-----------------Part
2 3 ---------------à | |||||||||
|
Submitted by: |
|
Name of GCL’s Designated Person |
|
Signature: |
|
|
|
Date: |
|
|
|
Received by: |
|
Name and Signature of the SOR |
|
Post: |
|
|
|
Date & Time |
|
|
Remark:
1) For the term contract, if
there are no full time site supervisory staff, the Supervising Officer’s
Representative should spot check and then sign as appropriate in accordance with
paragraph 25 of DEVB TC(W) 6/2010.
2) Part 1 - The GCL shall
complete Part 1 in duplicate and a copy should be kept by the Supervising
Officer’s Representative.
3) Part 2 - The GCL shall
complete Part 2 and submit the whole summary to the Supervising Officer’s
Representative within 1 working days after the records are posted at the EPD
website.
|
APPENDIX M Environmental Mitigation Implementation Schedule for Waste
Management |